The intelligence of large language models, while powerful, is often 'spiky' and unpredictable. Harness engineering aims to shape this raw capability into reliable performance for specific tasks. It's less about the model itself and more about the intricate system built around it—the prompts, tools, and execution flows designed to optimize metrics like task completion, efficiency, and speed.
From Top 30 to Top 5: A Harness Overhaul
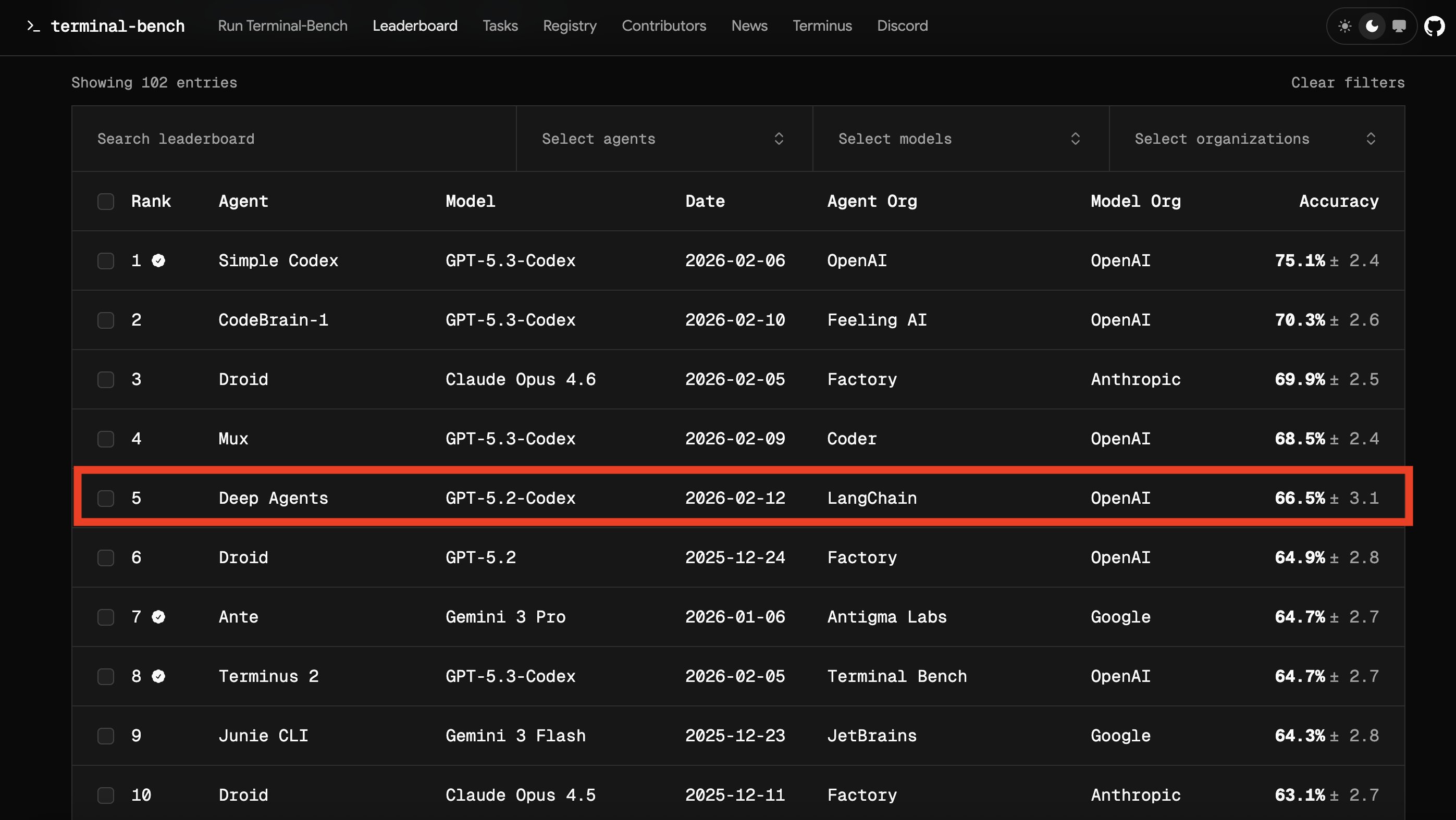
Researchers at LangChain demonstrated the impact of harness engineering by significantly boosting their coding agent, deepagents-cli. By exclusively refining the 'harness'—the system surrounding the GPT-5.2-Codex model—they improved its score on the Terminal Bench 2.0 from 52.8 percent to 66.5 percent, propelling it from outside the top 30 to the top 5.
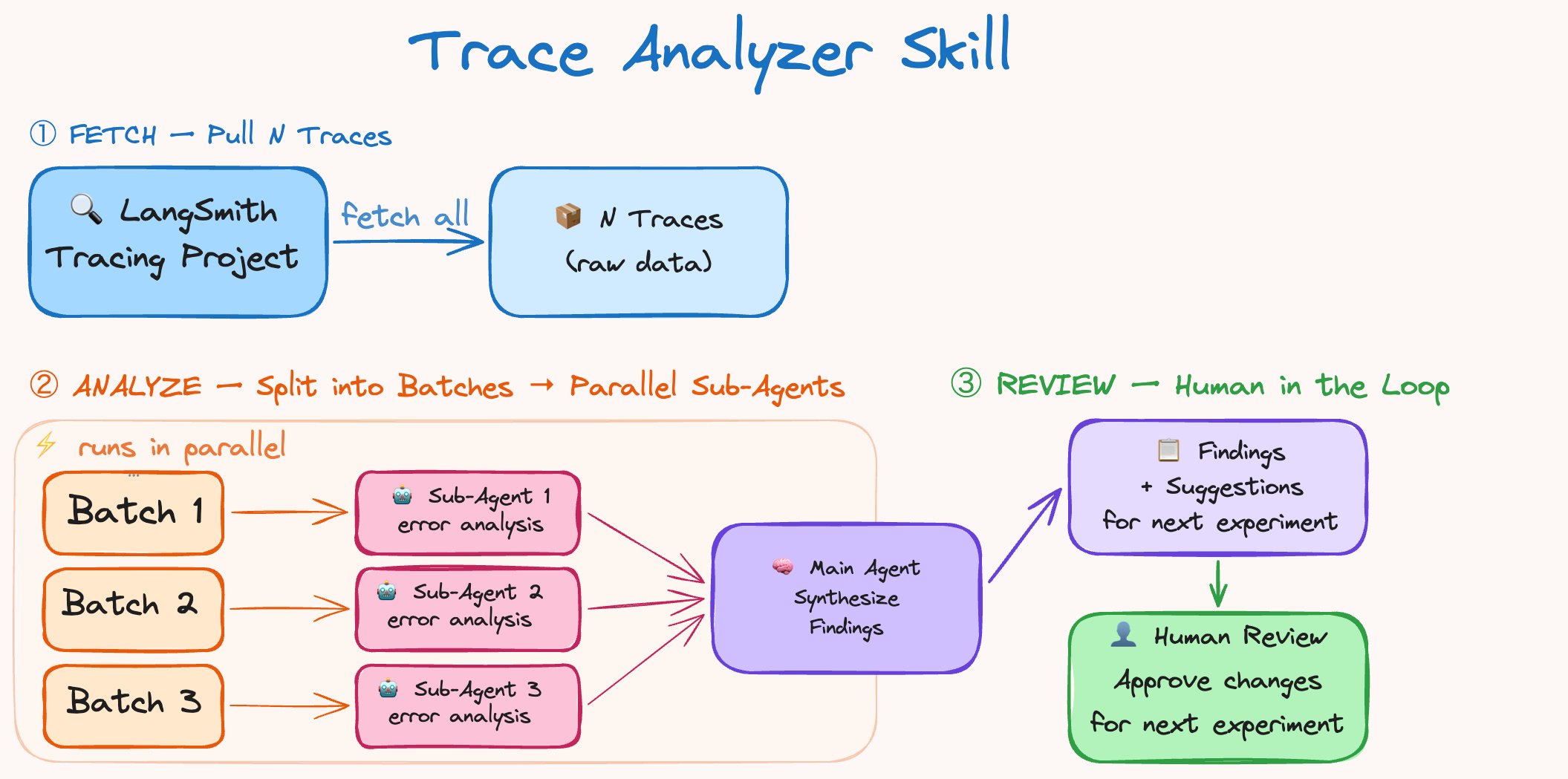
The key was understanding agent failures. Models are often black boxes, but their inputs and outputs, captured through tracing tools like LangSmith, provide crucial data for improvement cycles.
The 'Knobs' of Harness Design
An agent's harness offers numerous adjustment points: system prompts, tool selection, middleware (hooks around model and tool calls), and more. LangChain focused on three primary areas: the system prompt, available tools, and middleware.
Starting with a default setup, the agent scored 52.8 percent. The team then implemented an 'Trace Analyzer Skill' to systematically identify and address errors across multiple runs. This process mirrors the concept of boosting in machine learning, focusing improvement efforts on past mistakes.
Automated Analysis Fuels Performance Gains
Automated trace analysis allowed for rapid debugging of issues ranging from reasoning errors to instruction adherence failures. This systematic approach revealed common pitfalls, such as agents writing code and then prematurely deeming it correct without thorough verification.
Building and Self-Verifying Code
A critical insight was the need to engineer a 'build-verify' loop into agents. Models don't inherently prioritize testing. LangChain introduced guidance in the system prompt emphasizing a four-step problem-solving process: Planning, Building (including writing tests), Verifying against the task specification, and Fixing errors.
A 'PreCompletionChecklistMiddleware' was added to intercept the agent before completion, forcing a final verification pass against the task requirements. This is akin to adding an external checkpoint to ensure the agent doesn't exit prematurely.
Context is King
Harness engineering also involves delivering the agent its environment effectively. This includes mapping directory structures, identifying available tools (like Python interpreters), and injecting this context to reduce the agent's search and error surface. Prompting agents to write testable code and adhere to specific file path requirements also significantly improves reliability.
Time constraints are another crucial environmental factor. Injecting time budget warnings nudges agents to shift focus from implementation to verification, mimicking real-world project management.
Stepping Back from Doom Loops
Agents can get stuck in 'doom loops,' repeatedly making minor, ineffective changes to the same code. A 'LoopDetectionMiddleware' tracks file edits and can prompt the agent to reconsider its approach after a certain threshold, helping to break these cycles.
Optimizing Compute for Reasoning
The amount of computational power dedicated to an agent's reasoning process impacts performance. LangChain experimented with different reasoning modes, finding that a 'reasoning sandwich'—high reasoning for planning and verification, with medium for execution—yielded the best results, avoiding timeouts while ensuring thoroughness.
The ultimate goal of the harness engineer is to prepare and deliver context, enabling agents to autonomously and effectively complete tasks within defined constraints.
Practical Principles for Agent Harnesses
Several key takeaways emerged from this work:
- Context Engineering: Agents need explicit onboarding with environmental details, tools, and best practices.
- Self-Verification: Prompting agents to rigorously test and refine their work is crucial, especially without human oversight.
- Tracing as Feedback: Analyzing agent traces is vital for debugging both tooling and reasoning processes.
- Guardrails: Designing around current model limitations, like blind retries or lack of verification, builds immediate robustness.
- Model Tailoring: Harnesses should be iterated upon for specific models and tasks to maximize performance.
The future of harness design likely involves multi-model systems and enhanced memory capabilities for continual learning. LangChain is open-sourcing its Deep Agents project and sharing its trace dataset to foster further research in this evolving field.