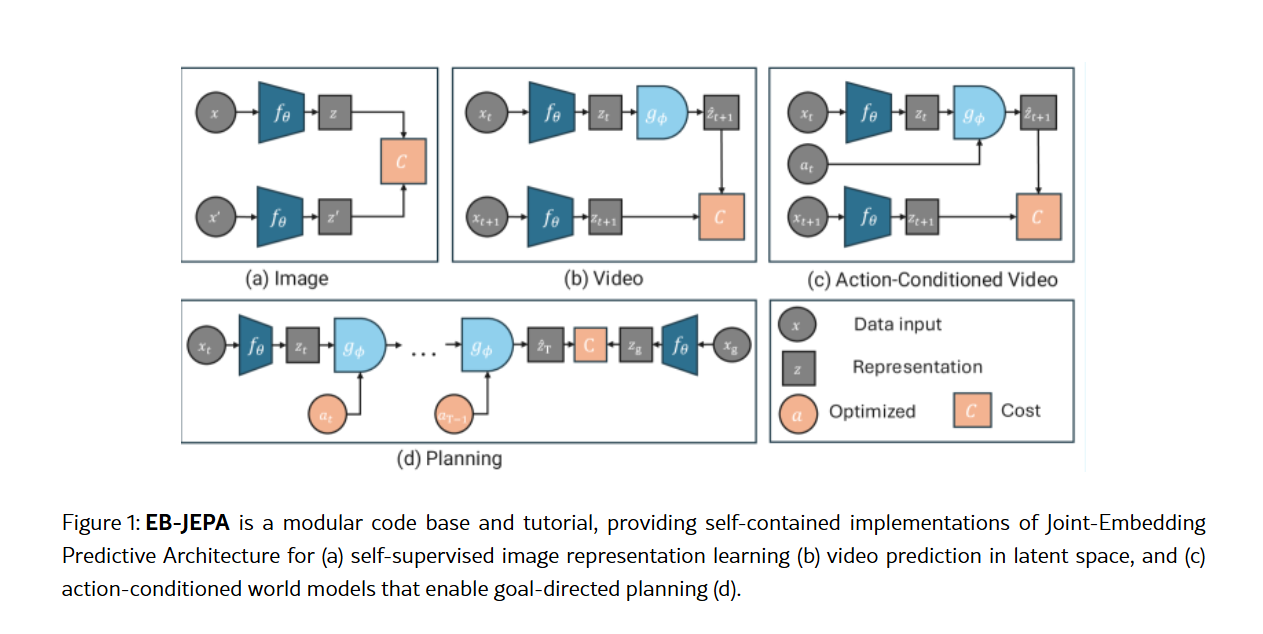
Meta AI researchers have released EB-JEPA, an open-source library designed to democratize the development of sophisticated AI world models. Built around Joint-Embedding Predictive Architectures (JEPAs), the library offers modular implementations for learning representations and predicting future states, moving beyond pixel-level reconstruction to focus on semantically meaningful features.
This new toolkit aims to lower the barrier to entry for researchers and educators, enabling complex self-supervised learning tasks on a single GPU within hours. The library covers three progressively challenging areas: image representation learning, video prediction, and action-conditioned planning.
Making AI World Models Accessible
Traditional generative models often get bogged down in pixel-level details, requiring immense computational power. JEPAs sidestep this by learning to predict within a compressed, semantic representation space. This approach, detailed in the paper, avoids the pitfalls of generative modeling while capturing features crucial for downstream tasks.
The EB-JEPA library provides modular implementations for self-supervised image learning, latent video prediction, and action-conditioned world models for planning.
The EB-JEPA library provides a unified framework that builds on energy-based models. It learns by minimizing prediction error in representation space, incorporating regularization techniques like VICReg and SIGReg to prevent model collapse. This allows for stable training without relying on negative samples, a common challenge in contrastive learning.
From Images to Actionable Planning
The library showcases its versatility through three core examples. First, image representation learning on CIFAR-10 demonstrates how JEPAs can extract robust features, achieving 91% accuracy in linear probing tasks. This highlights the effectiveness of self-supervised representation learning, a field where EB-JEPA offers valuable new tools.
Next, Video-JEPA extends these principles to temporal dynamics using Moving MNIST. The model learns to predict future video frames in representation space, showcasing scalability to time-series data. Finally, an action-conditioned world model tackles the Two Rooms navigation task, achieving a 97% planning success rate. This demonstrates the library's capability in building models that can plan and act in environments.
Modular Design and Educational Focus
A key contribution of EB-JEPA is its modular architecture. Reusable components for encoders, predictors, and regularizers allow researchers to easily combine and adapt them for new applications. The library includes comprehensive documentation and ablation studies, providing practical guidance on hyperparameter tuning and revealing the critical importance of each regularization component for preventing representation collapse.
The authors emphasize EB-JEPA’s role as an educational resource. By offering concise, single-GPU-trainable examples, they aim to make energy-based self-supervised learning more accessible for research and teaching. Future work could explore hierarchical world models and learned cost functions, further extending the capabilities demonstrated by this foundational library.