A new report from Akamai reveals that OpenAI has cemented its position as the single largest source of automated traffic hitting the internet, accounting for 42.4% of all measured AI bot requests—more than double the volume generated by its nearest competitor.
The data, analyzed by Akamai’s Tom Emmons in the latest AI Pulse report, paints a picture of an AI ecosystem increasingly centralized around one vendor. While four major platforms make up 90% of all AI bot traffic, OpenAI’s sheer volume and operational diversity set it apart from rivals like Anthropic and Perplexity.
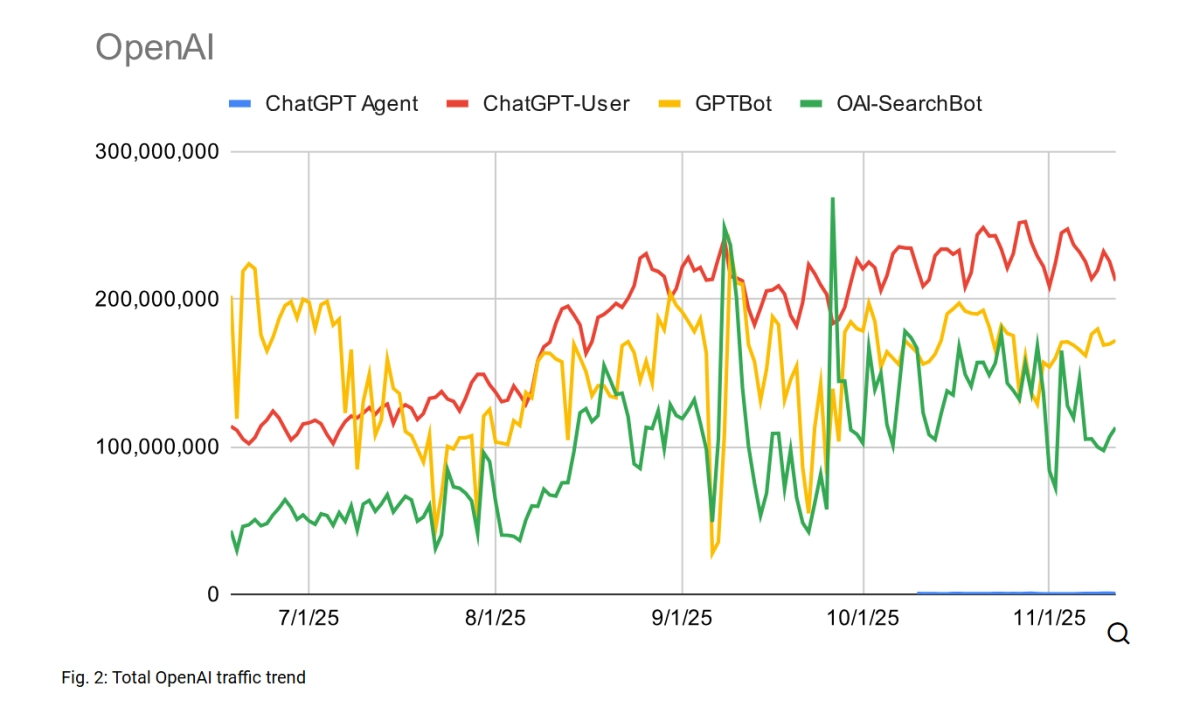
OpenAI isn't just running a single training crawler; it acts as a "generalist," deploying a layered fleet of four distinct bots: the foundational GPTBot for training, the OAI-SearchBot for indexing, the lightweight ChatGPT-Agent for task execution, and the high-volume ChatGPT-User for real-time data fetching.
This variety is key. Where Anthropic’s traffic is almost entirely dominated by its training crawler, and Perplexity is primarily a search crawler, OpenAI has significant, meaningful traffic across training, search, and user-driven retrieval. This blended approach gives OpenAI a persistent, multifaceted presence across the web that no other vendor currently matches.
The Fetcher Problem
The most immediate operational headache for web publishers and e-commerce sites isn't the training crawler, however. It’s the ChatGPT-User bot.
This fetcher is responsible for real-time retrieval when users or integrated applications request fresh information via the API or live data lookups. According to Akamai’s findings, while all OpenAI bots trigger some mitigation, the volume and percentage of blocking actions are dramatically higher for ChatGPT-User.
This makes intuitive sense: fetchers hit sensitive endpoints like inventory, pricing, and content APIs, often at high frequency tied to real-user activity. As a result, customers are actively fighting this traffic.
The data shows a clear escalation in defensive measures. Outright denial (blocking) experienced the steepest rise in October, coinciding with a spike in overall OpenAI bot traffic. More notably, nearly two out of every three advanced mitigation actions—including "tarpitting" (intentionally slowing down the bot) and "serve slow"—across all AI bots are attributed specifically to ChatGPT-User.
For organizations, this means the era of passively accepting AI bot traffic is over. OpenAI’s footprint is now too large and too diverse to ignore. Companies must establish clear strategies—whether that means allowing the training crawler but throttling the user-driven fetcher—to manage the overwhelming volume and high-intent requests driven by the world’s dominant AI platform.