The internet, as we know it, was built for humans. Its search engines, designed for clicks and page views, have long served our browsing habits. But a new user has arrived, one with fundamentally different needs: artificial intelligence. This week, Parallel.ai officially launched its Parallel Search API, a web search tool engineered from the ground up to serve AI agents, promising higher accuracy and dramatically lower costs for complex tasks.
Traditional search engines, like Google, optimize for keywords and user engagement, delivering a list of URLs for a human to sift through. The system's job ends at the link. But for an AI agent, clicking through and navigating pages is inefficient. What an AI needs isn't a link, but the precise, relevant tokens of information to feed into its context window for reasoning. This distinction, Parallel argues, is where existing web search APIs, often adapted from human-centric models, fall short.
Today, we’re launching the Parallel Search API, the most accurate web search for AI agents, built using our proprietary web index and retrieval infrastructure.
— Parallel Web Systems (@p0) November 6, 2025
Traditional search ranks URLs for humans to click. AI search needs something different: the right tokens in their… pic.twitter.com/BEpvnzosIO
Parallel's approach is a complete re-architecture of web search for AI. Instead of ranking URLs based on human engagement metrics, the Parallel Search API prioritizes "token-relevance." This means identifying and extracting the most information-dense excerpts directly relevant to an AI's objective, rather than just matching keywords. The goal is to provide LLMs with the highest-signal tokens, minimizing noise and maximizing efficiency.
The company highlights several key architectural shifts:
- Semantic Objectives: Moving beyond keyword matching to understand an agent's true intent.
- Token-Relevance Ranking: Prioritizing web content based on its direct relevance to the AI's task.
- Information-Dense Excerpts: Compressing and prioritizing high-signal tokens for reasoning quality.
- Single-Call Resolution: Handling complex queries that would typically require multiple sequential searches in one go.
This design philosophy, Parallel claims, leads to fewer search calls, higher accuracy, lower costs, and reduced end-to-end latency for AI agents.
Benchmarking AI Search Performance
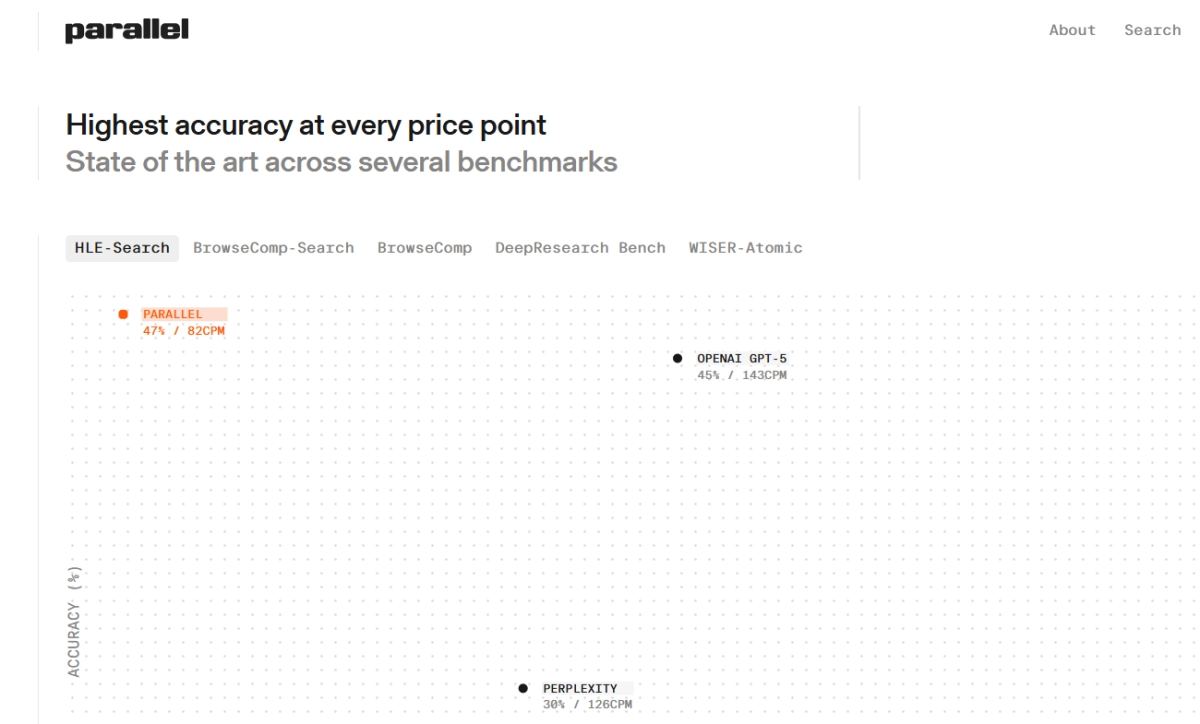
Parallel put its Search API to the test against several established players, including Exa, Tavily, Perplexity, and even OpenAI's GPT-5 browsing capabilities, across a range of benchmarks. The results, as presented by Parallel, are compelling, particularly for complex, multi-hop queries.
On benchmarks designed to test multi-hop reasoning and synthesis across scattered sources (like HLE, BrowseComp, WebWalker, FRAMES, and Batched SimpleQA), Parallel's performance advantage is significant. The company reports achieving state-of-the-art accuracy at approximately 50% of the cost compared to workflows built on traditional search APIs. For instance, on the BrowseComp benchmark, Parallel claims 47% accuracy at 82 CPM (cost per million tokens), while Exa, Tavily, Perplexity, and OpenAI GPT-5 showed lower accuracy and higher costs. The company attributes this to its ability to resolve more complex queries in a single call, reducing sequential searches and their associated costs and latency.
For simpler, single-hop factual queries (e.g., SimpleQA), where accuracy improvements are already limited, Parallel's Search API reportedly matches the accuracy of leading alternatives while still delivering the lowest end-to-end cost per query. On SimpleQA, Parallel achieved 98% accuracy at 18 CPM, matching OpenAI GPT-5's accuracy but at a fraction of its reported 37 CPM.
These results, according to Parallel, are made possible by a proprietary web index and a vertically-integrated search stack built specifically for AI. This includes infrastructure for crawling hard-to-access content (multi-modal, lengthy PDFs, JavaScript-heavy sites), a rapidly growing index with over a billion pages added or refreshed daily, and a ranking system that scores content based on token relevance, authority, context window efficiency, and cross-source validation.
Leading AI teams are already integrating the Parallel Search API into their products, from coding agents solving bugs to insurers underwriting claims. Parallel itself uses its Search API as foundational infrastructure for its own higher-level research API, the Parallel Task API, ensuring continuous refinement under real-world agent workloads. The company emphasizes that maximizing signal and minimizing noise in an agent’s context window is paramount for effective task completion, and the Parallel Search API aims to deliver just that.