Gravis Robotics AG announced the closure of a $23 million funding round dedicated to scaling its artificial intelligence solutions for earthmoving equipment. IQ Capital and Zacua Ventures jointly managed this investment, signaling sustained investor interest in construction automation technology. Pear VC, Imad, Sunna Ventures, Armada Investment, and Holcim also participated in the financing.
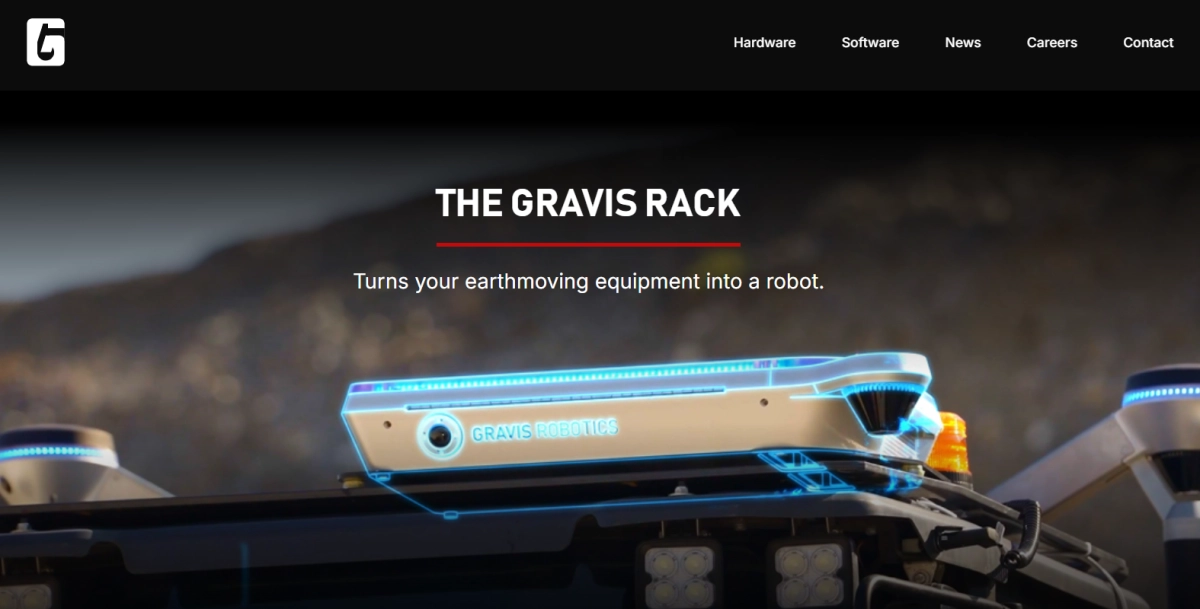
The company’s core offering is the Gravis Rack, a modular hardware system designed to retrofit excavators and similar machinery with partial autonomy capabilities.
This system integrates a computing appliance containing the necessary AI processing hardware, cameras, and LiDAR sensors, mounted typically on the vehicle roof.
Operators interface with the equipment through a proprietary tablet interface called Slate, enabling remote control or supervision of automated tasks. A key technological differentiator is the system's enhanced positioning accuracy, achieved through GNSS RTS technology integrated into rear masts alongside additional sensors. This method analyzes raw GPS radio signals to correct standard location errors, often achieving sub-inch precision crucial for detailed earthmoving operations.
Furthermore, these masts incorporate Wi-Fi transmitters necessary for synchronizing real-time data streams between the vehicle sensors and the operator’s Slate tablet. The Slate tablet provides operators with augmented supervision, overlaying crucial data like utility locations onto live sensor feeds, thereby minimizing the risk of infrastructure strikes during excavation. Users can execute complex actions, such as loading soil onto dump trucks, through simple touchscreen interactions or traditional joystick and pedal controls.
The AI stack automates sequencing, including identifying and positioning near the target dump truck for efficient material transfer. Chief Executive Officer Ryan Luke Johns commented that the technology allows operators to seamlessly transition between full autonomy and augmented control, accelerating operational adoption while building a robust dataset from difficult field jobs. Gravis Robotics reports current customer adoption across four continents, including major industrial players like HD Hyundai Co. This funding is earmarked for expanding Gravis Robotics’ international footprint and forging deeper integration partnerships with established construction equipment manufacturers.
The market for autonomous heavy machinery is intensifying, pushing incumbent construction technology firms toward similar automation strategies. The competitive landscape includes firms focusing on machine guidance and full autonomy solutions for construction sites, where operational efficiency and labor substitution remain primary drivers for investment. Consequently, Gravis’s strategy of offering a retrofittable, partial autonomy kit targets a broad, immediate need within the existing fleet infrastructure.
The company’s immediate objective involves leveraging this capital to further refine the Slate interface for complex scenarios and onboard new capabilities derived from real-world operational data gathered through its growing international deployment base.