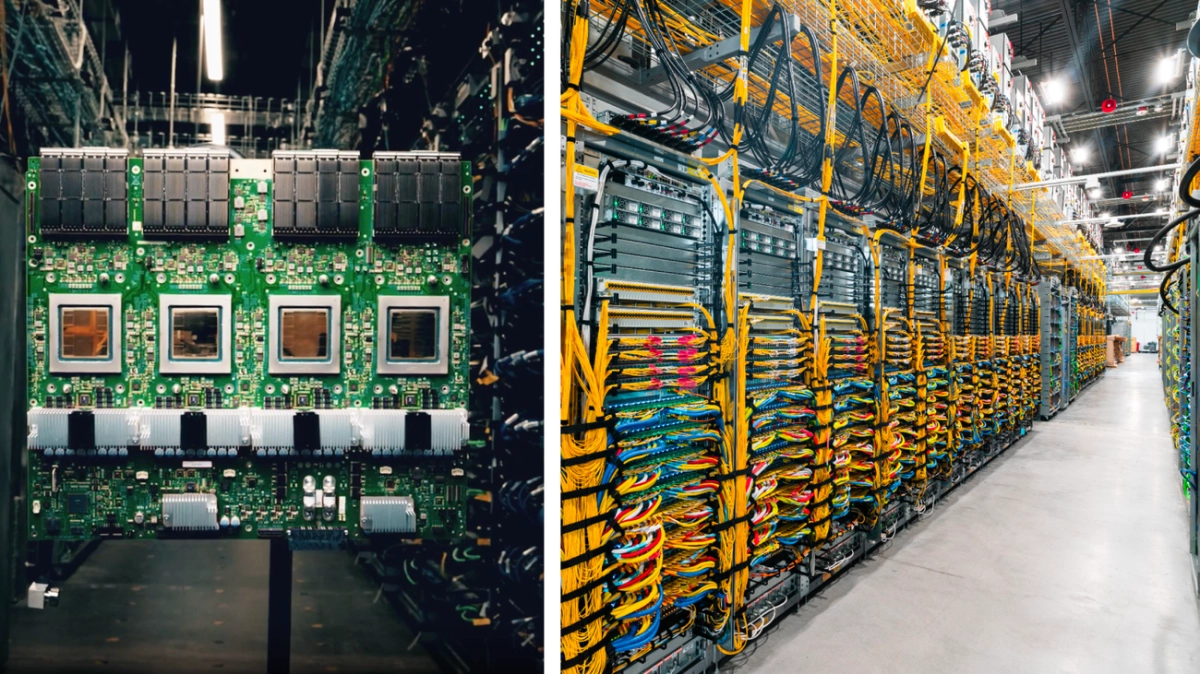
Google has officially launched Ironwood, its seventh-generation Tensor Processing Unit (TPU), making it available to Cloud customers. This latest custom silicon is engineered for the demanding requirements of modern AI, focusing on raw power and energy efficiency. Ironwood is positioned to accelerate the shift towards high-volume, low-latency AI inference, marking a significant step in Google's hardware strategy.
The industry's focus is rapidly evolving from training massive frontier models to deploying them for responsive, real-world interactions. Ironwood directly addresses this need, purpose-built for high-volume inference and model serving. According to the announcement, it delivers over 4X better performance per chip for both training and inference workloads compared to its predecessor, a substantial leap that directly impacts the speed and smoothness of complex AI services running in the cloud.
Ironwood's architecture is not just about individual chip performance; it's about a massive, interconnected system. These TPUs form the backbone of Google's AI Hypercomputer, grouping individual units into "superpods" that can scale up to 9,216 chips. This immense network is linked by a breakthrough Inter-Chip Interconnect (ICI) operating at 9.6 Tb/s, ensuring rapid communication and access to a staggering 1.77 Petabytes of shared High Bandwidth Memory (HBM). This design effectively eliminates data bottlenecks, drastically reducing the compute-hours and energy needed for cutting-edge AI.
The AI-Driven Design Advantage
Google's approach to hardware development, particularly with its Google TPU line, stands apart due to its integrated research and development loop. Unlike competitors who often rely on external vendors, Google DeepMind researchers collaborate directly with TPU engineers to influence architectural advancements. This synergy ensures that Google's latest models, like Gemini, are optimized for and trained on the newest TPU generations, yielding immediate and significant speedups. Furthermore, Google employs an AI-driven method called AlphaChip, which uses reinforcement learning to generate superior chip layouts, a technique responsible for the last three TPU generations, including Ironwood.
The arrival of Ironwood underscores Google's commitment to controlling its AI infrastructure stack from silicon to software. This vertical integration provides a distinct competitive advantage, enabling Google to deliver highly optimized and energy-efficient AI services to its cloud customers. Expect Ironwood to power more sophisticated, responsive, and scalable AI applications across Google Cloud, setting a new benchmark for inference performance in the industry.