Google is rolling out significant Android accessibility enhancements, with its Gemini AI models playing a pivotal role, according to the announcement. These updates, shared ahead of International Day of Persons with Disabilities, aim to make devices more intuitive and helpful for a wider range of users. The deep integration of Gemini signals a significant shift towards AI-driven inclusive design on the platform.
The most impactful Google Gemini accessibility integration appears in the Pixel camera's Guided Frame feature. Previously offering basic object detection, Gemini now provides rich, contextual descriptions, transforming a simple "face in frame" into detailed narratives like "One girl with a yellow T-shirt sits on the sofa and looks at the dog." This shift from mere identification to nuanced environmental understanding represents a significant advancement for blind or low-vision users, offering enhanced independence and confidence in capturing moments. It underscores AI's potential to bridge sensory gaps with sophisticated interpretative capabilities.
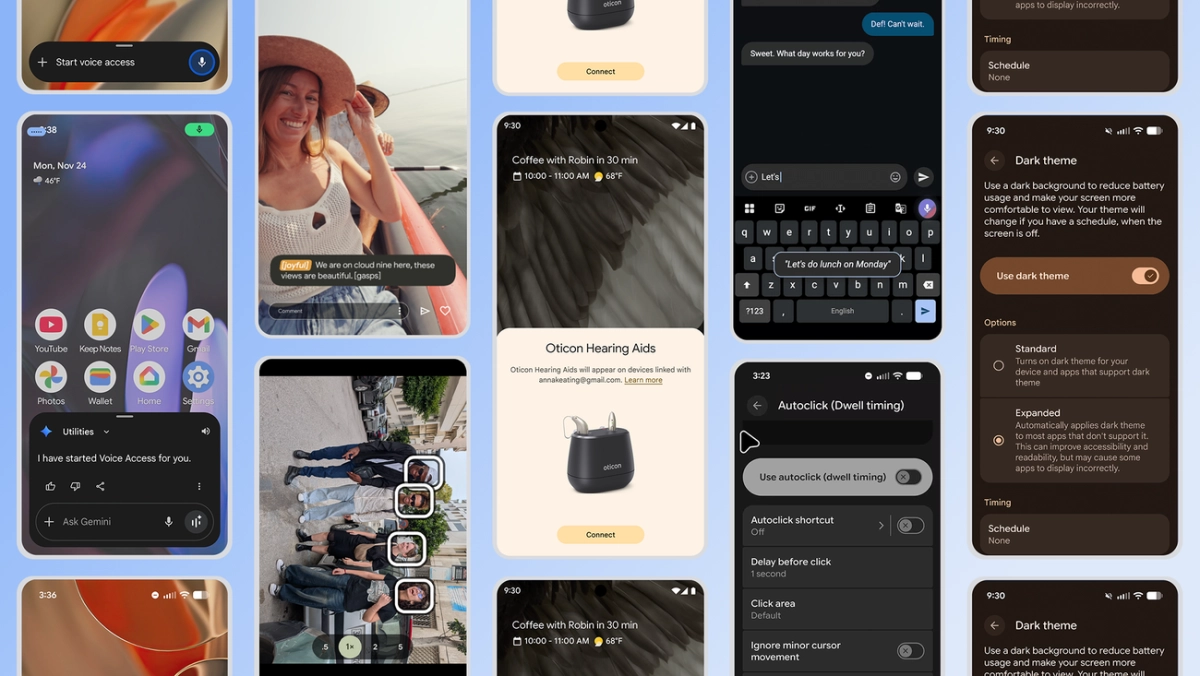
Gemini also significantly refines Voice Access, addressing a long-standing user challenge for Google Gemini accessibility. The ability to activate Voice Access hands-free with a simple "Hey Google, start Voice Access" eliminates the physical tap requirement, a critical barrier for many. Beyond activation, Gemini-powered improvements enhance voice typing command recognition, including punctuation, and adapt to diverse accents and speech patterns automatically. This expanded linguistic intelligence and seamless initiation significantly redefines hands-free device interaction, moving towards a truly frictionless user experience.
Beyond Gemini: A Holistic Accessibility Push
While Google Gemini accessibility takes center stage, Google's broader Android accessibility initiative extends across several crucial areas. The expanded dark theme option, now automatically darkening most apps regardless of native support, offers a more consistent and comfortable viewing experience for users with low vision or light sensitivity. Expressive Captions, leveraging AI, now detect and display emotional tone, adding vital context to conversations and media, a feature also extending to YouTube. These updates collectively demonstrate a commitment to comprehensive inclusion, addressing diverse needs from visual comfort to nuanced communication.
Further enhancing physical interaction, AutoClick's improved dwell cursor allows for customizable delay times and click types, significantly reducing physical strain for mouse users. For TalkBack users, a simple two-finger double-tap will soon activate Gboard voice dictation, streamlining text input. Crucially, the introduction of Fast Pair for Bluetooth LE Audio-enabled hearing aids simplifies connectivity with a single tap, a key enhancement for users relying on assistive listening devices. These granular improvements collectively reduce friction across various interaction modalities, making Android more universally usable.
Google's latest Android accessibility features, particularly the deep integration of Gemini, mark a significant milestone for inclusive technology. By leveraging advanced AI, Google is moving beyond basic assistive functions to provide more intelligent, contextual, and proactive support. This strategic investment in AI-powered accessibility not only enhances the daily lives of millions but also establishes a new industry standard for how sophisticated models can be deployed to foster genuine digital equity. The future of accessibility is clearly intertwined with the continuous evolution of AI capabilities.