Anthropic is making a bet of staggering proportions on Google Cloud, announcing plans to expand its use of Google Cloud TPUs to an unprecedented one million chips. This monumental commitment, valued at tens of billions of dollars, is set to bring well over a gigawatt of compute capacity online in 2026, dramatically escalating the AI compute arms race.
The move underscores the insatiable demand for AI infrastructure as companies like Anthropic race to build and serve ever more capable models. For Anthropic, the expansion is critical to meet the exponentially growing demand from its customer base, which now includes over 300,000 businesses and a nearly 7x increase in large accounts (over $100,000 in run-rate revenue) in the past year alone.
Anthropic CFO Krishna Rao highlighted the long-standing partnership with Google, stating the expansion "will help us continue to grow the compute we need to define the frontier of AI." This increased capacity isn't just about scale; it's also intended to power more thorough testing, alignment research, and responsible deployment of its Claude models.
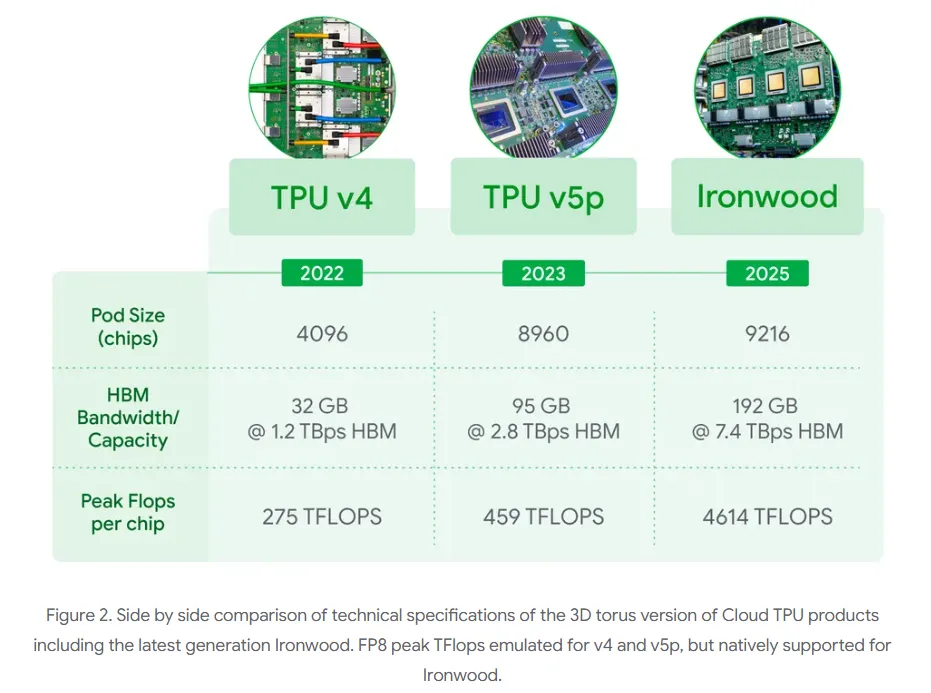
Google Cloud CEO Thomas Kurian emphasized that Anthropic's decision reflects "the strong price-performance and efficiency its teams have seen with TPUs for several years." Kurian also pointed to Google's continued innovation in its AI accelerator portfolio, including the seventh-generation TPU, codenamed Ironwood, which will likely be a key component of this expansion.
The Compute Arms Race and a Multi-Cloud Reality
While this expansion is a massive win for Google Cloud, Anthropic maintains a nuanced, diversified compute strategy. The company explicitly states its approach "efficiently uses three chip platforms–Google’s TPUs, Amazon’s Trainium, and NVIDIA’s GPUs." This multi-platform stance is designed to ensure continued advancement of Claude's capabilities while maintaining strong partnerships across the industry.
Notably, Anthropic reiterated its commitment to Amazon as its "primary training partner and cloud provider," continuing work on Project Rainier, a massive compute cluster with hundreds of thousands of AI chips across multiple U.S. data centers. This suggests that while Google Cloud TPUs are now a colossal piece of Anthropic's infrastructure puzzle, they are part of a broader, strategic distribution of compute resources.
The deal, initially announced as a strategic partnership in 2023, has already seen thousands of businesses, including Figma, Palo Alto Networks, and Cursor, utilize Claude models on Google Cloud's Vertex AI platform and Marketplace. This latest expansion solidifies Google's position as a critical enabler for one of the leading generative AI developers, further validating its custom-built TPU architecture against the dominance of NVIDIA's GPUs.
For the broader AI industry, this Anthropic Google Cloud TPUs deal signals that the compute arms race is far from over, and indeed, is intensifying. Companies are willing to invest staggering sums to secure the necessary infrastructure, pushing cloud providers to innovate rapidly and offer competitive, specialized AI accelerators. The future of AI will be built on an unprecedented scale of computational power, and Anthropic is clearly hedging its bets across the best available options.