Thinking Machines Lab has unveiled a significant advancement in large language model post-training, introducing on-policy distillation LLMs as a highly efficient method for developing specialized, high-performing smaller models. According to the announcement, this approach combines the direct learning benefits of on-policy training with the rich feedback of distillation, addressing critical limitations of existing methods. The innovation promises to make expert LLM capabilities more accessible and cost-effective for a wider range of applications. This development marks a pivotal shift in how developers can refine LLMs for specific tasks and domains.
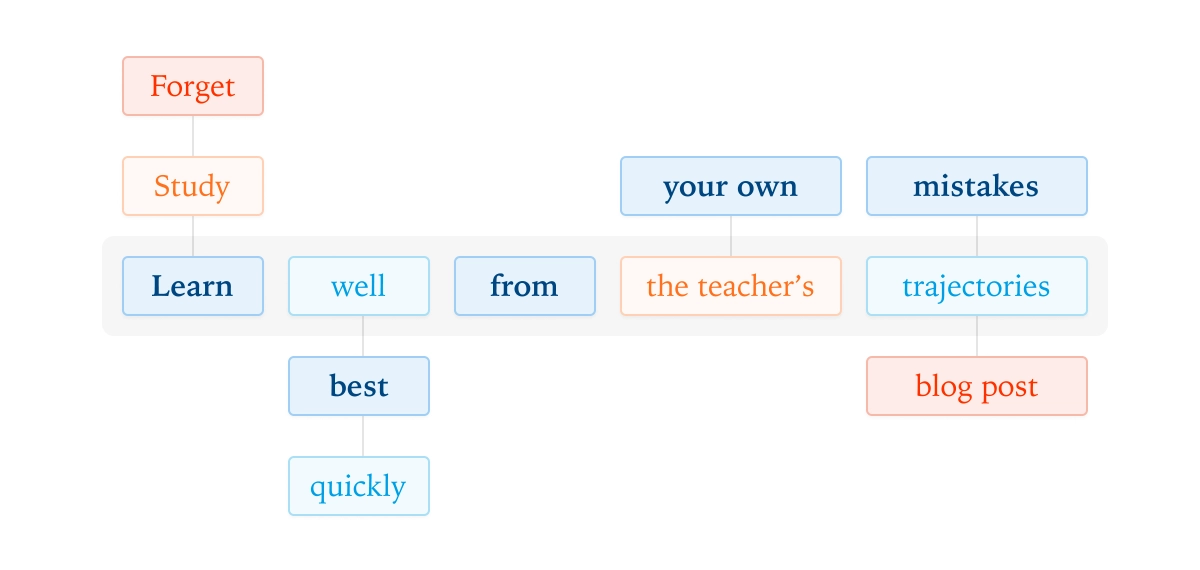
Historically, post-training LLMs has involved a trade-off between two primary approaches: reinforcement learning (RL) and off-policy distillation. RL, an on-policy method, allows models to learn from their own generated trajectories, directly addressing their mistakes. However, its sparse feedback, often just a single win/loss signal per episode, makes it notoriously inefficient for complex tasks like multi-step reasoning. Conversely, off-policy distillation, typically supervised fine-tuning (SFT) on teacher-generated data, offers dense, token-level feedback. Its major flaw lies in the student model learning from contexts the teacher frequents, not necessarily the divergent states the student itself might encounter, leading to compounding errors and a potential imitation of style over substance.
The core innovation of on-policy distillation LLMs is its ability to bridge this gap. By sampling trajectories directly from the student model, it ensures relevance to the student's actual behavior. A high-performing teacher model then provides dense, token-level feedback, grading each step of the student's reasoning process. This is analogous to a chess grandmaster analyzing every move a novice makes, rather than just observing perfect play or receiving a simple win/loss outcome. This granular feedback allows the student to learn precisely where mistakes occur, accelerating the learning process significantly.
Efficiency and Practical Applications
The computational efficiency of on-policy distillation LLMs is a standout feature. The Thinking Machines Lab team replicated results from the Qwen3 team, demonstrating that on-policy distillation can achieve equivalent performance on reasoning benchmarks at a fraction of the cost of traditional RL. Specifically, the method showed a 9-30x cost reduction in FLOPs compared to off-policy SFT, and a substantial reduction in GPU hours. This efficiency stems from using a reverse KL divergence loss function, which is "mode seeking" and "unhackable," pushing the student to approximate the teacher's behavior in every state it encounters.
Beyond raw efficiency, on-policy distillation LLMs prove invaluable for personalization and continual learning. Training smaller models on new domain knowledge often leads to catastrophic forgetting, where previously learned instruction-following or chat behaviors degrade. On-policy distillation effectively recovers these lost behaviors by using an earlier, capable version of the model as a teacher to "re-invoke" lost skills. This phase-alternating approach allows models to continuously update with new knowledge without sacrificing their core capabilities, a critical need for enterprise applications and evolving data environments.
The implications for the LLM industry are profound. On-policy distillation LLMs democratize access to advanced post-training techniques, enabling smaller organizations to develop highly specialized and efficient models without the prohibitive costs associated with large-scale RL or extensive proprietary datasets. This method facilitates the creation of compact, domain-expert models that can be deployed locally for enhanced privacy and security, updated more easily, and operated at significantly lower inference costs. It represents a practical pathway to building more robust, adaptable, and economically viable LLM solutions for diverse real-world challenges.