This October was filled with big announcements from leaders in the autonomous vehicle industry. Waymo announced it had integrated its sixth-gen, fully autonomous tech, the Waymo Driver, into Hyundai's all-electric IONIQ 5 SUV. Elon Musk unveiled a new robotaxi capable of self-driving, predicting it would be available by 2027. These are just a few of many developments happening under the hood of the market.
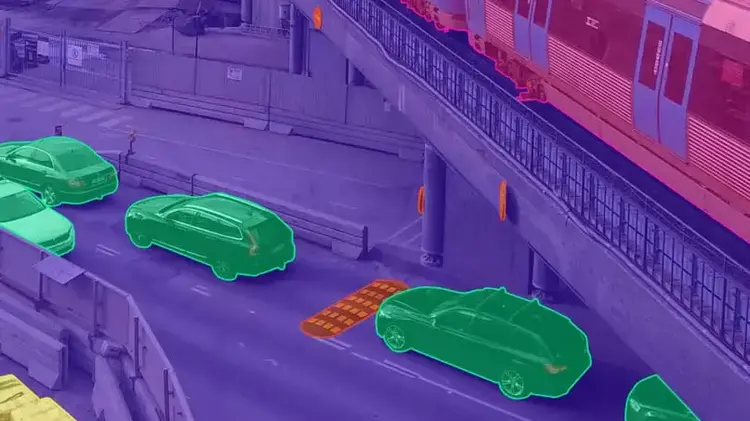
Autonomous vehicles heavily rely on deep neural networks trained with massive labeled datasets. Meticulous annotation of various elements within sensor data provides the fundamental building blocks for these AI algorithms. High-quality annotations allow the models to learn and increase their prediction accuracy over time, leading to safer and more reliable self-driving cars.

Types of Data Used for Autonomous Vehicles
IEEE paper says that autonomous vehicles are expected to save almost half a million lives between 2035 and 2045. Moreover, since 90% of the accidents are caused by humans, 9% by weather and road conditions, and only 1% by vehicular failures, autonomous vehicles will provide much safer traffic, drastically decreasing the number of accidents.
Autonomous vehicles depend on their sensor systems to perceive the surrounding objects and environment. It highlights the scale of data required and reinforces the demand for detailed annotation to cover countless scenarios.
Here’s an overview of the key data types used and their role in advancing these systems.
Camera Images and Video Streams
Camera data is essential for autonomous vehicle perception. High-resolution images and video streams offer detailed information about the surroundings. This includes road conditions, traffic signs, pedestrians, and other vehicles. Advanced computer vision and data annotation train machine learning algorithms to detect and classify objects in real-time.
LiDAR Point Clouds
LiDAR sensors create detailed 3D representations of the environment by emitting laser pulses. The resulting point clouds provide precise depth information. This allows autonomous vehicles to perceive the world in three dimensions. LiDAR data is key for obstacle detection, mapping, and localization tasks.
Radar and GPS Data
Radar sensors provide accurate measurements of object distances and velocities. This is vital for detecting and tracking moving objects, even in challenging weather. GPS data helps determine the vehicle's precise location, aiding in mapping and localization tasks.
Sensor fusion — combining data from LiDAR, radar, and camera systems — improves object detection accuracy. This process enables autonomous vehicles to better detect obstacles, enhancing safety and functionality, particularly in challenging weather conditions.
Waymo announced it had integrated its sixth-gen, fully autonomous tech, the Waymo Driver, into Hyundai's all-electric IONIQ 5 SUV. It will be gradually added to the Waymo One fleet. It will include six cameras, five lidar sensors, six radar units, and an array of external audio receivers (EARs). These sensors will cover all around the vehicle, up to 500 meters. They will work day and night, in all weather. That’s the equivalent of over five football fields of visible range.

Data Annotation Techniques for Self-Driving Cars
The choice of annotation technique depends on the specific requirements of the autonomous driving system and the type of data being processed. Companies can efficiently annotate large datasets by combining multiple techniques and leveraging automation tools while maintaining high accuracy and consistency.
Here are some of the most popular:
Bounding Boxes for Object Detection
Bounding box annotation is a key technique in self-driving cars. It involves drawing rectangular shapes around objects of interest in images or videos. This technique provides essential information about object location and size, enabling accurate detection and classification by machine learning models.
Semantic Segmentation for Scene Understanding
Semantic segmentation is another powerful technique used in self-driving cars. It assigns class labels to each pixel in an image, providing a detailed scene understanding. This technique is useful for identifying road boundaries, lane markings, and other critical elements. By leveraging semantic segmentation, autonomous vehicles can better understand their surroundings and make informed decisions.

Polygon annotation
Used for outlining complex shapes and irregular objects that cannot be accurately represented by rectangular bounding boxes.
3D cuboids
Employed to represent the three-dimensional dimensions of objects, providing valuable information for depth perception and distance estimation.
Landmark annotation
Involves identifying and labeling key points and distinctive features within an image, such as the corners of a traffic sign or the edges of a road.
Annotating Objects for Autonomous Driving
Annotating objects means labeling and categorizing elements in the vehicle's sensor data. By providing a detailed set of labeled data points, data annotation enables the creation of accurate HD maps. These maps are a reliable reference for self-driving cars. They help the cars understand and respond to their surroundings.
As Waymo says its autonomous vehicles have driven over 20 million miles on public roads, supported by over 20 billion miles of simulation data. It highlights the scale of data required and reinforces the demand for detailed annotation to cover countless scenarios.
Here are some of the elements for labeling.
Buildings, Vehicles, Pedestrians, and Cyclists
Among the most critical objects for autonomous vehicles to detect and track are other vehicles, pedestrians, and cyclists. By accurately identifying these dynamic entities, self-driving cars can predict their movements and adjust their trajectory.
Road Signs, Traffic Signals, and Lane Markings
In addition to moving objects, autonomous vehicles must also recognize and interpret static elements of the road infrastructure. Traffic sign classification is essential for understanding and adhering to speed limits, stop signs, yield signs, and other regulatory markers. Detecting traffic signals allows self-driving cars to navigate intersections safely and efficiently. Lane markings guide maintaining proper positioning within the vehicle's designated lane, enabling smooth and predictable navigation.

Features of Annotation for Autonomous Vehicles
Accurate maps and precise localization are vital for self-driving cars. They rely on HD maps to find their location and direction. Annotated datasets train SLAM algorithms. They enable vehicles to create and update maps in real time and to find their position. This is critical for navigation in dynamic environments.
Training autonomous vehicles with annotated data from diverse environments enhances their ability to handle real-world scenarios safely. By including rare cases like construction zones and unexpected pedestrian actions, these systems better manage critical situations.
Data annotation allows for continuous improvement. It integrates new data and real-world feedback. This keeps the AI updated for complex road conditions. It moves us closer to widespread self-driving adoption. Clear annotation guidelines are crucial to ensure consistent labeled datasets.

Rigorous quality control is vital for accuracy. It requires audits, cross-validation, and error checks. Experienced, domain-expert annotators reduce error risks. They accurately label complex scenarios, which strengthens self-driving systems.
Addressing class imbalance, where certain objects or scenarios are underrepresented, is another challenge. Strategic data collection and targeted annotation mitigate this imbalance, ensuring diverse and representative datasets.
Keymakr's Expertise for Autonomous Vehicle Data Annotation
Keymakr's team of over 600 specialists have over 9 years of experience with data in the automotive domain, more than 90 completed large-scale projects, and 656 million annotated files. Its robust expertise allows the team to give some tips to all companies that are looking for reliable providers.
- Choose Providers Skilled in Diverse Annotation Tools and Techniques
Ensure the provider has experience with multiple data types for autonomous driving. These include high-definition camera images, video streams, LiDAR point clouds, radar, and GPS data. Working with a partner proficient in advanced tools like 3D point cloud annotation and sensor fusion techniques can significantly enhance data quality for autonomous vehicles. - Select a Team Equipped to Handle Large, Complex Datasets Efficiently
Autonomous vehicle data annotation requires managing extensive data volumes and multi-sensor inputs under tight deadlines. Look for teams with proven expertise in data processing pipelines and scaling, capable of meeting rigorous timelines without compromising on data quality. - Prioritize Quality with Robust QA Processes
Autonomous vehicle models depend on precise, high-quality data. A meticulous QA process ensures annotated data is reliable and accurate, providing the foundation for safer, more effective AV models. Keymakr’s emphasis on a 4-level QA process with custom sanity scripting ensures exceptional labeling accuracy. - Balance Automated and Human Annotation for Best Results
While automated annotation accelerates processing, human annotators play a critical role in refining data, especially with edge cases in autonomous driving scenarios. A hybrid approach using automated tools and human-in-the-loop can reduce costs and increase accuracy, vital for the nuanced requirements of model training. - Ensure Data Security & Privacy Standards are Met
Autonomous vehicle data often includes sensitive environmental and behavioral data. Choose ISO-certified providers with strict data protection protocols. Providers like Keymakr, with an in-house annotation team and proprietary annotation platform Keylabs, ensure a secure, controlled workflow to safeguard data integrity.