The sheer velocity of artificial intelligence innovation continues to redefine technological frontiers, a fact powerfully underscored by Matthew Berman’s recent AI news roundup. From Meta’s ambitious leap into augmented reality glasses to OpenAI’s startling achievement in algorithmic problem-solving, the industry pulses with developments that are simultaneously groundbreaking and indicative of foundational shifts. This week’s highlights painted a vivid picture of a sector grappling with unprecedented demand, pushing the boundaries of what AI can perceive, generate, and process.
Meta is making a substantial bet on the glasses form factor, as evidenced by the leaked demo of their new Rayban glasses. These smart glasses promise an in-lens display, integrating AI that can "see the world, hear the world, and… project things onto a clear screen that only you can see." This vision of a personalized, always-on augmented reality interface, paired with Meta’s history in AR/VR, suggests a long-term commitment to embedding AI directly into our daily visual and auditory experiences, aiming to make technology an invisible assistant rather than a separate device.
A stark demonstration of AI’s rapidly advancing cognitive abilities came from OpenAI, whose reasoning system achieved a perfect 12/12 score during the 2025 ICPC World Finals, a premier collegiate programming competition. This feat, which would have placed it first among all human participants, utilized both GPT-5 and an experimental reasoning model. Scott Wu, CEO of Cognition, aptly summarized the achievement: "so insane. you guys have no idea how hard this is." This performance in complex algorithmic problem-solving highlights the emergent "superhuman intelligence" in specific domains, pushing the boundaries of what AI can autonomously achieve in tasks requiring deep logical deduction and problem-solving.
Further enhancing AI’s operational efficiency, Meta Superintelligence Labs published a paper detailing REFRAG, a method to accelerate Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG). By swapping most retrieved tokens for precomputed and reusable chunk embeddings, REFRAG improves RAG speed by 30x and fits 16x longer contexts without accuracy loss. This optimization is crucial for enterprise AI applications, enabling more efficient and contextually rich interactions with vast internal data repositories, moving beyond raw model intelligence to practical, scalable deployment.
The insatiable demand for AI infrastructure continues to fuel significant investment, with AI chip startup Groq raising $750 million at a post-funding valuation of $6.9 billion. This funding round, led by Disruptive and including major players like Blackrock and Neuberger Berman, will expand Groq’s data-center capacity, with new locations planned globally. Jonathan Ross, Groq’s CEO, noted the "unquenchable" thirst for inference capacity, underscoring a core insight: the physical infrastructure required to power advanced AI models is becoming as critical as the models themselves, driving a frenetic build-out across the industry.
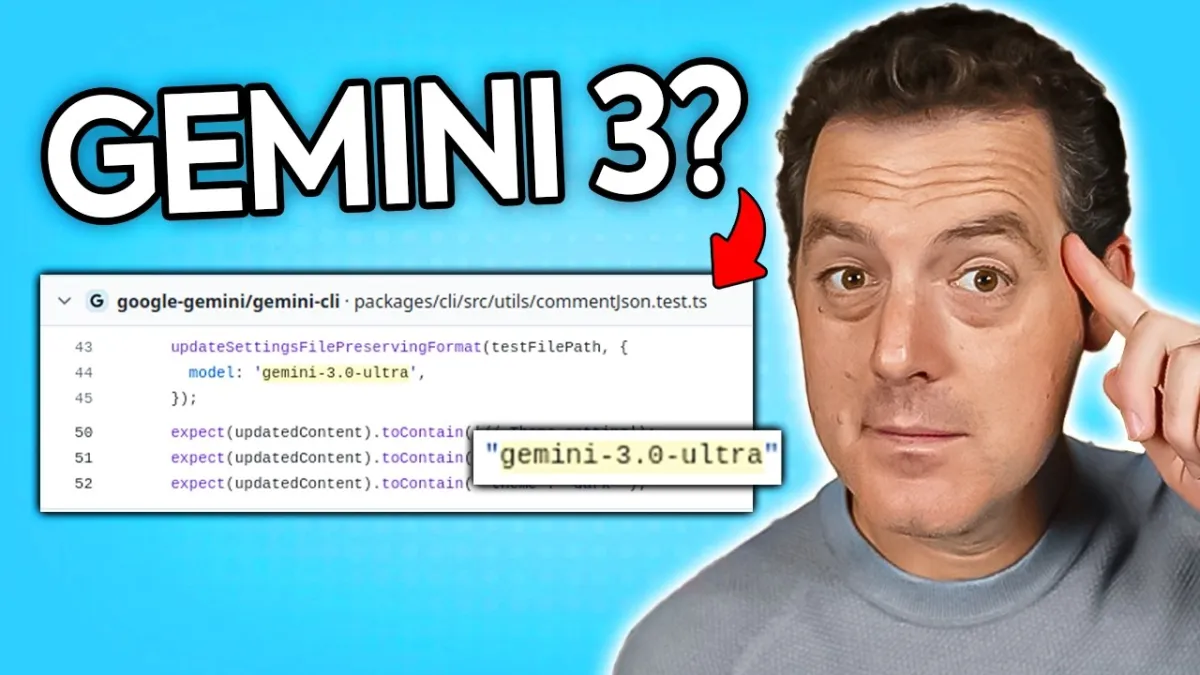
Meanwhile, the "rumor mill" surrounding Google’s Gemini 3.0 Ultra model suggests its imminent release, with evidence spotted in Google’s Gemini CLI repo. The anticipation for this new iteration of Gemini speaks to the intense competitive landscape in large language models. In a related development, new State-of-the-Art benchmarks were achieved on the ARC-AGI prize by Jeremy Berman and Eric Pang. Their open-source solutions, utilizing Grok 4 and novel program-synthesis outer loops with test-time adaptation, showcase the collaborative and iterative nature of AI research, where open-source contributions rapidly elevate collective capabilities.
Google is also extending AI’s reach into transactional realms with the announcement of its Agent Payments Protocol (AP2). This open, shared protocol facilitates secure and compliant transactions between AI agents and merchants. With a growing list of major partners including Adobe, PayPal, and Salesforce, AP2 lays the groundwork for an AI-driven economy where autonomous agents can conduct financial transactions, hinting at a future where AI handles more than just information processing. Concurrently, Fei-Fei Li’s World Labs demonstrated a spatial AI company capable of generating immersive 3D worlds from single images, offering a glimpse into AI’s potential for creating vast, explorable digital environments.
The democratization of AI-powered content creation tools is also accelerating. Tongyi Lab launched DeepResearch, the first fully open-source Web Agent that achieves performance on par with OpenAI’s Deep Research, but with a significantly smaller footprint (only 30 billion parameters, with 3 billion activated). This agent demonstrates state-of-the-art results across various benchmarks, notably scoring 32.9 on Humanity's Last Exam. This achievement, built on an automated, multi-stage data strategy without costly human annotation, exemplifies the trend of scaling AI capabilities without human bottlenecks. On another front, Google DeepMind made its Veo 3 Fast model available for YouTube Shorts creators, enabling AI-generated video clips with sound. While initially novel, this development raises questions about the long-term impact of AI-generated content, with some speculating about a "tsunami of AI slop" that will eventually require human curation and a renewed focus on "taste."
Tencent Hunyuan’s launch of Hunyuan3D 3.0, featuring 3x higher precision and ultra-HD voxel modeling for stunning detail, further pushes the boundaries of 3D content generation. This tool promises lifelike facial contours and professional-grade visuals for designers and creators. Simultaneously, the demand for OpenAI’s GPT-5-Codex has surpassed forecasts, leading to calls for more GPUs and the unfortunate necessity to run Codex 2x slower than targets. This bottleneck highlights a persistent challenge: the physical infrastructure, particularly GPUs, struggles to keep pace with the exponential demand for advanced AI processing.
Finally, the increasing sophistication of physical AI was showcased by a video of a humanoid robot demonstrating remarkable agility, quickly recovering its balance after being deliberately pushed and kicked. This display of robust physical control underscores the rapid advancements in robotics and embodied AI, moving towards machines capable of navigating and interacting with the physical world with increasing autonomy and resilience. The continuous, rapid evolution across these diverse AI domains confirms that the technological landscape is not merely changing, but fundamentally transforming at an unprecedented pace, driven by both groundbreaking research and relentless market demand.