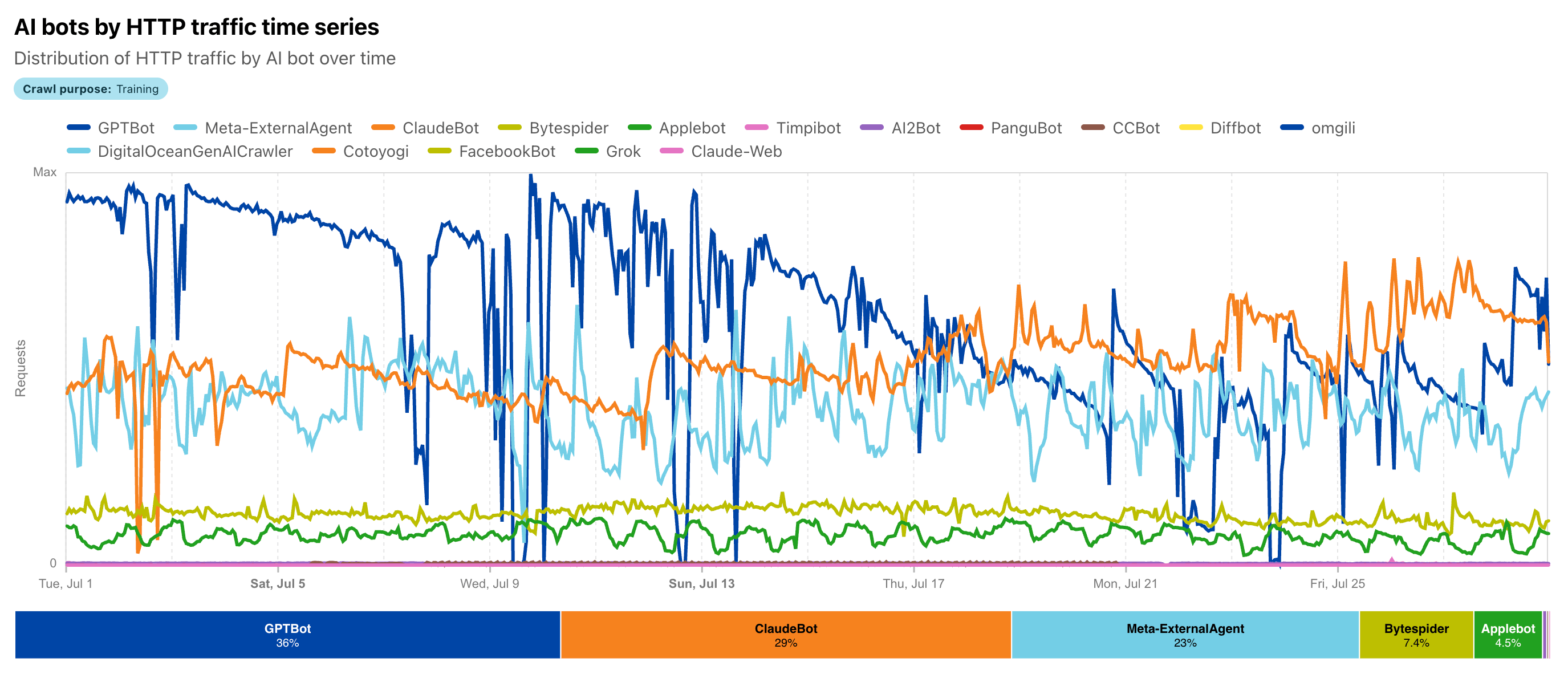
AI bot traffic has exploded to unprecedented levels in 2025, with new data from Cloudflare and Fastly revealing that artificial intelligence crawlers now account for nearly 80% of all AI bot traffic across the web.
This dramatic surge is fundamentally reshaping how content flows through the internet, and threatening the economic foundation that has sustained web publishing for decades.
The Shocking Scale of AI Bot Traffic Growth
The numbers paint a stark picture of transformation. From May 2024 to May 2025, AI bot traffic grew by 18% overall, with some individual crawlers showing explosive growth rates exceeding 300%. Meta's AI crawlers alone now generate 52% of all AI crawler traffic, more than double the combined traffic from Google (23%) and OpenAI (20%).
But it's the intensity that's most concerning. Fetcher bots, those that access content in response to user queries, can hit websites with over 39,000 requests per minute, placing enormous pressure on server infrastructure and sometimes mimicking DDoS attacks without malicious intent.
The Economic Disruption Behind AI Bot Traffic
The traditional web publishing model is crumbling under the weight of this AI bot traffic surge. For decades, search engines crawled websites with an implicit promise: show up in search results, get traffic, earn ad revenue. But AI platforms are breaking that bargain.
Cloudflare's new crawl-to-refer ratios reveal the stark reality: some platforms show ratios as extreme as 70,900:1, meaning for every 70,900 times an AI system crawls content, it refers back just one visitor to the source site. The disparity is staggering across major AI platforms:
- Anthropic (Claude): 50,000:1 to 70,900:1 crawl-to-refer ratio
- OpenAI (ChatGPT): 152:1 to 887:1 ratio
- Perplexity: 32.7:1 to 118:1 ratio
Publisher Revenue Under Siege from AI Bot Traffic
Recent data from Digital Content Next shows that Google AI Overviews are linked to traffic drops of up to 25% for publisher members, with the median year-over-year decline in Google Search referrals hitting -10% overall. Major news and entertainment brands are seeing consistent week-over-week declines, with losses outpacing gains by a 2:1 ratio.
The impact varies dramatically by industry:
- News and media sites face more balanced but still concerning crawler activity, with referral ratios ranging from 32.7:1 to 2,500:1
- Computer and electronics sites see different patterns, with Amazon's bot moving into second place behind OpenAI's GPTBot
- E-commerce and high-tech sectors face the highest levels of AI bot traffic for training data collection
The Infrastructure Cost of AI Bot Traffic
The Read the Docs project discovered that blocking AI crawlers decreased their traffic by 75%, dropping from 800GB to 200GB daily and saving approximately $1,500 per month in bandwidth costs. This example illustrates the hidden financial burden AI bot traffic places on website operators.
Unlike traditional search crawlers that follow predictable patterns, AI bot traffic exhibits more aggressive behaviors. Infrastructure maintainer Dennis Schubert notes that AI crawlers "don't just crawl a page once and then move on, they come back every 6 hours", multiplying resource consumption without clear rationale.
The Training vs. Fetching Divide in AI Bot Traffic
The data reveals two distinct categories within AI bot traffic:
Training Crawlers (80% of AI bot traffic):
- Aggressively scrape content to build AI models
- Show irregular activity patterns with sustained increases lasting days or weeks
- Often ignore robots.txt directives
- Generate massive bandwidth consumption
Fetcher Bots (20% of AI bot traffic):
- Respond to specific user prompts in real-time
- OpenAI's ChatGPT-User bot accounts for nearly 98% of fetcher traffic, showing clear daily usage cycles
- Create massive request spikes that can overwhelm servers
- Represent users asking AI systems to fetch information rather than visiting websites directly
Regional Patterns and Industry Impact of AI Bot Traffic
North America receives nearly 90% of observed AI bot traffic activity, suggesting concentrated impact on English-language content and North American publishers. The commerce, media, entertainment, and high-tech sectors face the highest levels of scraping activity.
According to DoubleVerify, general invalid traffic rose by 86% in the second half of 2024 due to AI crawlers, with 16% of bot impressions in 2024 generated by AI scrapers like GPTBot, ClaudeBot, and AppleBot.
The Response: New Tools and Policies for Managing AI Bot Traffic
Website operators are fighting back with new strategies:
Technical Solutions:
- Google-Extended robots.txt directives to separate AI training from search indexing
- Advanced firewall rules targeting cloud provider IP ranges
- Real-time monitoring for unusual traffic patterns and bandwidth spikes
Business Responses:
- Cloudflare has introduced new crawl-to-refer ratio tracking and AI Insights dashboards
- Some platforms are exploring monetization models for AI access
- Publishers are demanding separate crawler controls for search versus AI training
What This Means for the Future of Web Content
The AI bot traffic surge represents more than a technical challenge, it's a fundamental shift in how information flows through the internet. As AI systems become primary endpoints for user queries rather than intermediaries directing traffic to source sites, the economic model supporting web content creation faces existential pressure.
Key implications include:
- Revenue model disruption: Traditional search-traffic-ads pipeline increasingly circumvented
- Attribution erosion: Content synthesized and presented without meaningful source credit
- Infrastructure strain: Massive server loads generating no revenue for content creators
- Discovery transformation: Users increasingly query AI systems rather than browsing websites directly
The Road Ahead for AI Bot Traffic Management
Work is underway to allow website publishers to declare how automated systems should use their content, though standardization and adoption will take time. The challenge extends beyond technical solutions to fundamental questions about fair value exchange in an AI-mediated web.
As Fastly's security research team notes: "AI bots are reshaping how the internet is accessed and experienced, introducing new complexities for digital platforms. Whether scraping for training data or delivering real-time responses, these bots create new challenges for visibility, control, and cost".
The data suggests we're witnessing the early stages of a transformation as significant as the rise of search engines—but this time, the traffic may not be coming back. Publishers who understand and adapt to AI bot traffic patterns today will be better positioned for whatever digital publishing landscape emerges from this upheaval.
AI bot traffic isn't just growing, it's fundamentally reshaping the web's economic and technical foundation. Content creators, website operators, and digital marketers must act now to understand, measure, and manage this new reality before it manages them.