Cisco's 2024 Data Privacy Benchmark Study revealed Generative AI is being adopted with both enthusiasm and caution in the enterprise.
Surveying 2,600 security and privacy professionals across 12 countries, the technology of Generative AI is becoming a staple, with 55% being very familiar and 41% somewhat familiar. In contrast, 52% of consumers in the previous year's survey admitted to being unfamiliar with the technology. Despite this gap in awareness, enterprises aren't shying away from leveraging Generative AI's capabilities. 79% of respondents acknowledged they are deriving significant or very significant value from these tools.
Cisco itself has taken to the technology. In June last year, they announced new Generative AI integrations into its Collaboration and Security portfolios, enhancing enterprise productivity and simplification. These include AI-powered features in Webex for meeting summaries and efficient communication, alongside advanced tools in their Security Cloud for policy management and threat response. Last month, they also announced advancements in efficient inferencing for Large Language Models (LLMs) on [Cisco] UCS with Intel Xeon Scalable Processors; optimized AI infrastructure capable of handling the demanding computational needs of Generative AI.

However, this growing integration of Generative AI in business operations doesn't come without its risks. 92% of organizations view Generative AI as a fundamentally different technology that introduces novel challenges and concerns, primarily in managing data and risk. The top concerns revolve around the potential harm to an organization’s legal and intellectual property rights, 69%, the risk of sensitive information being shared publicly or with competitors, 68%, and the accuracy of the information returned by these AI tools, 68%.
Despite understanding these risks, many users of Generative AI are entering sensitive data into these applications, abdicating their responsibility for judicious usage. 62% of respondents have inputted information about internal processes, 48% entered non-public company information, and 45% and 38% inputted employee and customer details, respectively – data that could be crippling if shared externally.
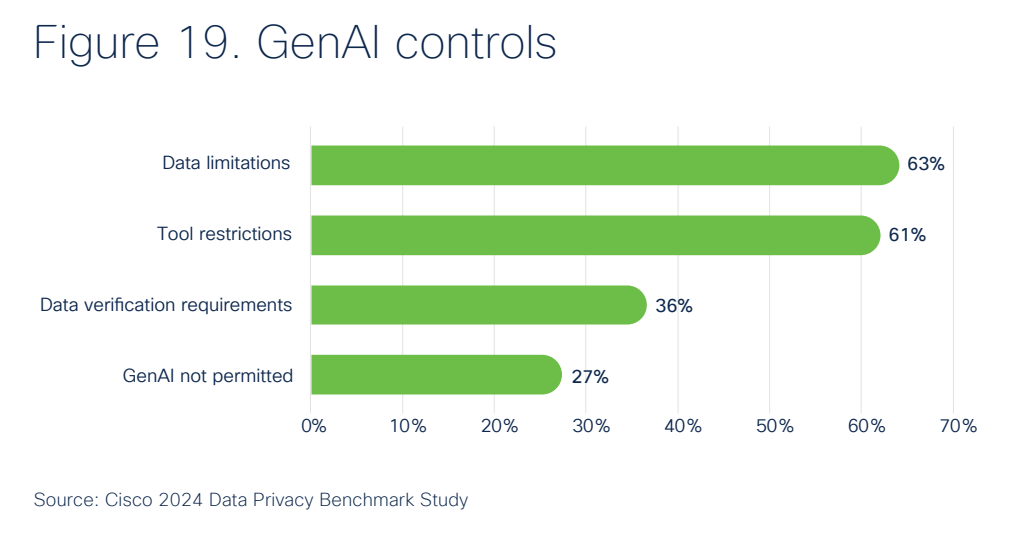
In response to these concerns, most organizations are implementing mitigating controls. 63% have established limitations on data entry into Generative AI tools, and 61% have restricted the use of certain Generative AI tools by employees. The most striking survey result was that 27% have imposed bans on Generative AI applications, at least temporarily. It's a reflection of the cautious but proactive approach to harnessing the benefits of Generative AI while safeguarding against its risks.
Acknowledging that while the survey provides insights into enterprise's cautious approach to Generative AI tools, it was conducted in the summer of 2023. As we approach the end of January 2024, the technological landscape, particularly in the realm of Generative AI, has evolved significantly. It's evolving on a weekly basis. The snapshot of that time period likely evolved considerably since, encapsulating the state of data, privacy and adoption to a lesser degree.